Home
Products
Sulfuretin


| Product Name | Sulfuretin |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN05162 |
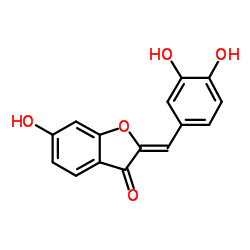
| CAS No.: | 120-05-8 |
| Molecular Formula: | C15H10O5 |
| Molecular Weight: | 270.24 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Flavonoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The herbs of Rhus verniciflua |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | Oc1ccc2c(c1)O/C(=Cc1ccc(c(c1)O)O)/C2=O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Sulfuretin inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing the NF-κB pathway. Sulfuretin can be used for the research of allergic airway inflammation. Sulfuretin reduces oxidative stress, platelet aggregation, and mutagenesis[1]. Sulfuretin is a competitive and potent inhibitor of monophenolase and diphenolase activities with the IC50 of 13.64 μM[2]. |
| In Vitro | Sulfuretin is one of the main flavonoids produced by Rhus verniciflua. Sulfuretin efficiently inhibits the infiltration of inflammatory cells and attenuates allergic airway inflammation. |
| In Vivo | Sulfuretin inhibits the inflammatory responses by suppressing the NF-κB pathway in type 1 diabetes models. Sulfuretin (40 μg/kg; single intraperitoneal injection 2 h after the last OVA challenge) suppresses ovalbumin (OVA)-induced chemotaxis and airway inflammation[1]. Animal Model: Pathogen-free male BALB/c mice (7-8 weeks old)[1] Dosage: 40 μg/kg Administration: A single intraperitoneal injection was administered 2 h after the last OVA challenge Result: Suppressed OVA-induced chemotaxis and airway inflammation. |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 585.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 228.8±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 270.052826 |
| PSA | 86.99000 |
| LogP | 1.98 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |