Home
Products
Amphotericin B


| Product Name | Amphotericin B |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN06595 |
| CAS No.: | 1397-89-3 |
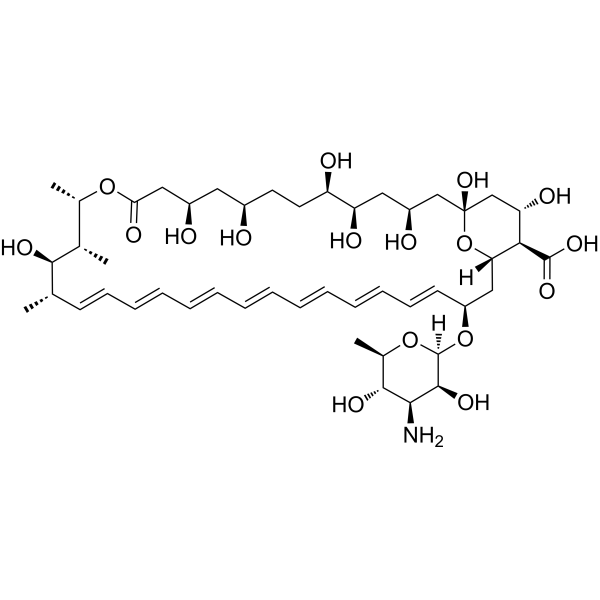
| Molecular Formula: | C47H73NO17 |
| Molecular Weight: | 924.07 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Miscellaneous |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | From Streptomyces nodosus |
| Solvent: | DMSO, Pyridine, Methanol, Ethanol, etc. |
| SMILES: | O[C@@H]1CC[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)C[C@H](O)C[C@]2(O)C[C@H](O)[C@H]([C@@H](O2)C[C@H](/C=C/C=C/C=C/C=C/C=C/C=C/C=C/[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H](OC(=O)C[C@@H](C1)O)C)C)O)C)O[C@@H]1O[C@H](C)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]1O)N)O)C(=O)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Amphotericin B is a polyene antifungal agent against a wide variety of fungal pathogens. It binds irreversibly to ergosterol, resulting in disruption of membrane integrity and ultimately cell death. |
| Target | Fungal[1] |
| In Vitro | Amphotericin B administration is limited by infusion-related toxicity, including fever and chills, an effect postulated to result from proinflammatory cytokine production by innate immune cells. Amphotericin B induces signal transduction and inflammatory cytokine release from cells expressing TLR2 and CD14[1]. Amphotericin B interacts with cholesterol, the major sterol of mammal membranes, thus limiting the usefulness of Amphotericin B due to its relatively high toxicity. Amphotericin B is dispersed as a pre-micellar or as a highly aggregated state in the subphase[2]. Amphotericin B only kills unicellular Leishmania promastigotes (LPs) when aqueous pores permeable to small cations and anions are formed. Amphotericin B (0.1 mM) induces a polarization potential, indicating K+ leakage in KCl-loaded liposomes suspended in an iso-osmotic sucrose solution. Amphotericin B (0.05 mM) exhibits a nearly total collapse of the negative membrane potential, indicating Na+ entry into the cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | Amphotericin B results in prolonging the incubation time and decreasing PrPSc accumulation in the hamster scrapie model. Amphotericin B markedly reduces PrPSc levels in mice with transmissible subacute spongiform encephalopathies (TSSE)[4]. Amphotericin B exerts a direct effect on Plasmodium falciparum and influences eryptosis of infected erythrocytes, parasitemia and hostsurvival in murine malaria. Amphotericin B tends to delay the increase of parasitemia and significantly delays host death plasmodium berghei-infected mice[5]. |
| Cell Assay | The kinetics of cell death induced by AmB against Leishmania promastigotes is followed by using fluorometry with the DNA-binding compound ethidium bromide (EB). Fluorescence measurements are performed on a SPEX Fluorolog II spectrophotometer at 365-580 nm excitation-emission wavelengths. Promastigotes at a final concentration of 25×106 cells/mL are incubated for 5 min with gentle stirring in the fluorescence cuvette with 2 mL of different buffered solutions but always containing 10 mM glucose and EB (50 mM). After signal stabilization is achieved, AmB is added and dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide. Maximal EB incorporation is always obtained by adding digitonin (50 mg/mL). All solutions used are buffered with 75 mM TRIS (pH 4 7.6) and contain 150 mM NaCl (BNa+), 150 mM KCl (BK+), 150 mM choline chloride, and 100 mM sucrose, 100 mM NaCl. The osmolarity of all solutions is always adjusted to 390±5 mOsm using an advanced instrument SW2 osmometer. |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 1140.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 643.5±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 923.487854 |
| PSA | 319.61000 |
| LogP | 1.16 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |