Home
Products
Dehydroglyasperin C
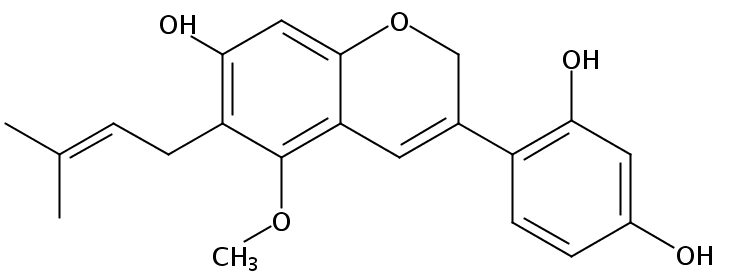


| Product Name | Dehydroglyasperin C |
| Price: | $657 / 5mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN04750 |
| CAS No.: | 199331-35-6 |
| Molecular Formula: | C21H22O5 |
| Molecular Weight: | 354.4 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Flavonoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The roots of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Dehydroglyasperin C, a isoflavone, is a potent NAD(P)H:oxidoquinone reductase (NQO1) and phase 2 enzyme inducer. Dehydroglyasperin C has antioxidant, neuroprotective, cancer chemopreventive, and anti-inflammatory activities[1][2][3]. |
| In Vitro | Dehydroglyasperin C (0.1-1 μM; 24 h) blocks the PDGF-induced progression through the G0/G1 to S phase of the cell cycle, and down-regulates the expression of CDK; 2, cyclin E, CDK4 and cyclin D1. Dehydroglyasperin C significantly attenuates PDGF-stimulated phosphorylation of PDGF receptor-β, phospholipase C-γ1, AKT and extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2, and DGC inhibits cell migration and the dissociation of actin filaments by PDGF[1]. Dehydroglyasperin C (0.1-1 μM; 24 h) treatment significantly decreases PDGF-induced cell number and DNA synthesis in a dose-dependent manner without any cytotoxicity in human aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMC)[1]. Cell Cycle Analysis[1] Cell Line: Human aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMC) Concentration: 0.1 μM, 0.5 μM, 1 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Blocked the PDGF-induced progression through the G0/G1 to S phase of the cell cycle. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: Human aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMC) Concentration: 0.1 μM, 0.5 μM, 1 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Down-regulated the expression of CDK; 2, cyclin E, CDK4 and cyclin D1. |
| In Vivo | In ICR mice, Dehydroglyasperin C (5 mg/kg; once) combined with CCl4 shows reduced lipid droplet formation in liver tissue, as assessed by histological examination. Further, DGC demonstrated a slight protective effect against centrilobular injury caused by CCl4 injection, perhaps through suppression of CYP2E1 expression[4]. |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 588.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 309.8±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 354.146729 |
| PSA | 79.15000 |
| LogP | 6.48 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |