Home
Products
Bryonolic acid
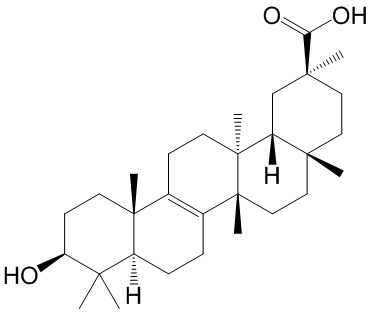


| Product Name | Bryonolic acid |
| Price: | $614 / 5mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN07992 |
| CAS No.: | 24480-45-3 |
| Molecular Formula: | C30H48O3 |
| Molecular Weight: | 456.7 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Triterpenoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The herbs of Sandoricum indicum |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Bryonolic acid is an active triterpenoid compound with immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anticancer activities[1][2][3]. |
| In Vitro | Bryonolic acid exerts anti-allergic activity by inhibiting homologous passive cutaneous anaphylaxis and delayed hypersensitivity. Bryonolic acid reduces nitric oxide by suppressing inducible nitric oxide synthase expression, indicating anti-inflammatory activity[1]. In rat adrenal pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells, Bryonolic acid against N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-induced neurotoxicity, indicating it as a candidate neuroprotective agent for cerebral ischemic treatment[1]. Bryonolic acid (1-200 μM) inhibits acyl-coA: cholesterol acyl transferase (ACAT) activity in rat liver microsomes in a concentration-dependent manner, blocking the biosynthesis of the cholesterol fatty acid ester tumour promoter. Bryonolic acid inhibits ACAT in intact cancer cells with an IC50 of 12.6 µM[2]. Bryonolic acid inhibits both clonogenicity and invasiveness in MCF-7 MB-231, U87 and 3T3-EA cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | Bryonolic acid (500 mg/kg; i.p.; once) potently induces HO-1 in a manner dependent on the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway[3]. Animal Model: Wild-type and Nrf2-/- mice[3] Dosage: 500 mg/kg Administration: i.p.; once Result: Induced HO-1 in a manner dependent on the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway. |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 553.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 302.5±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 456.360352 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 8.99 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.4 mmHg at 25°C |