Home
Products
Toosendanin
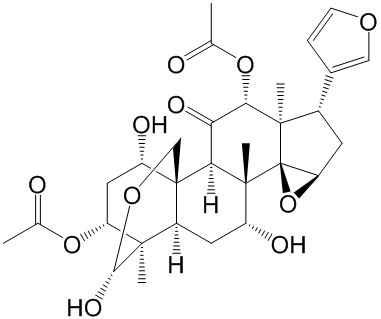


| Product Name | Toosendanin |
| Price: | $77 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN08061 |
| CAS No.: | 58812-37-6 |
| Molecular Formula: | C30H38O11 |
| Molecular Weight: | 574.62 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Triterpenoids |
| Physical Desc.: | White powder |
| Source: | The barks of Melia toosendan Sieb. et Zucc. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | CC(=O)O[C@H]1C(=O)[C@@H]2[C@@]34CO[C@H]([C@]([C@@H]4C[C@H]([C@]2([C@@]24[C@]1(C)[C@@H](C[C@H]4O2)c1ccoc1)C)O)([C@@H](C[C@@H]3O)OC(=O)C)C)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Toosendanin, a triterpenoid extracted from the bark of fruit of Melia toosendan Sieb et Zucc, possesses analgesic, insecticidal and anti-inflammatory activities[1]. |
| In Vivo | Toosendanin (0.5 and 1 mg/kg, Intraperitoneal injection daily for 7 days) alleviates DSS-induced experimental colitis by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization and regulating NLRP3 inflammasome and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling, and may provide a novel Chinese patent medicine for the treatment of murine colitis[1]. Animal Model: Forty-eight male C57BL/6 mice weighing 20-22 g[1]. Dosage: 0.5 and 1 mg/kg. Administration: Intraperitoneal injection daily for 7 days. Result: Protected against DSS-induced colitis in mice. Inhibited the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in DSS-induced UC and improved oxidative stress. |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 714.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 385.6±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 574.241394 |
| PSA | 165.26000 |
| LogP | -0.38 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |